Just like most storage mediums, partitioning a flash drive is also possible. There may be a number of reasons why you would want to partition a flash drive. If you have never partitioned a flash drive before, then don't worry; this article will help you. Read on to find how to partition a flash drive..
The Disk Utility’s Partitioning controls enable you to partition your MacBook’s disk. If you find yourself needing another volume on a disk — or if you need to resize the total space on existing volumes on a disk — click the Partition tab within Disk Utility to display the controls.
Partition with Diskpart
Partition with an USB Flash Drive Partition Tool
Bonus Tip 1. Best Way to Recover Files from Flash Drive after Partition or Format
1How to Partition Flash Drive on Windows10/8.1/8/7?
Although it is possible to create multiple partitions on a flash drive via third-party tools, Windows will only read and show the first/primary partition. If you want the Windows to read a certain partition of the flash drive, then you will need a third-party tool to set that partition as primary.
- Click the Partition Layout pop-up menu and choose the total number of volumes that you want on the selected disk. To add a partition to an existing layout, click the Add button (which carries a plus sign). Click the first volume block in the partition list (under the Partition Layout pop-up menu) to select it.
- Oct 16, 2019 However, you can’t write or delete files from a Mac. Aside from all that, NTFS has several cool features, including: It can have partitions as large as 16 million TB. You can store files as large as its partition size. It can work with Linux operating systems. Hierarchical File System Plus (HFS+) was developed by Apple for Mac OS X.
Backup Your Data
Partitioning a flash drive will erase all data stored on it. That's why it is highly recommended that you back up all the important data before proceeding. The backup process is quite easy as all you need to do is connect the flash drive to your computer and copy the desired data to a location of your choice. Follow these instructions:
1. Connect your flash drive to your computer. Then open This PC on your Windows and find your flash drive.
2. Double-click on it to see its contents. Select the files that you want to back up and right-click on them and click Copy.
3. After that, navigate to the folder on your computer's hard drive where you want to store those files, right-click and select the Paste option. The transfer process will begin and your selected files will be copied to that folder.
Now that you have backed up your data, you can proceed to partition your flash drive. Following are some methods to do this:
How To Check Partition Scheme
1Partition a Flash Drive Using Diskpart
You can easily partition a flash drive via the Diskpart utility of Windows. The utility is run through Command Prompt. Follow these instructions:
Step 1. Press Windows and R key on your keyboard at the same time and type 'diskpart' in the Run pop-up window and then press Enter to launch it. A command prompt window will open.
Step 2. On that window, input 'list disk' to see which number your connected flash drive has.
Step 3. Next, input 'select disk X (X here is the number for your flash drive). It will be selected.
Step 4. Now input 'clean' and press enter to clean the device.
Step 5. Now enter 'list part' and then input 'create partition primary'. After that, input 'list part' and then input 'select partition 1'. Set this partition as active by inputting 'active'.
Step 6. Next, input 'format fs=fat32' to format the partition. After that, your newly created flash drive partition will be ready to use.
2Partition a Flash Drive with an USB Flash Drive Partition Tool
If the method to partition a flash drive via diskpart seems complicated, then there is another easier way to partition a flash drive. You can partition the USB flash drive via a flash drive partition tool called Bootit. Follow these instructions to partition a flash drive via Bootit:
Fist, you should install and launch Bootit software on your computer.
Step 1. Connect your flash drive to your computer and make sure it is detected by the operating system.
Step 2. Now open Disk Management on your computer. You can launch it from the Start Menu.
Step 3. Now select the current partition shown on the flash drive and delete it via the software.
Step 4. After that, right-click on the unallocated space of flash drive and click on New Simple Volume to create a partition. You can specify the size, label, etc. for the new partition according to your preferences.
Step 5. You can create multiple partitions on your flash drive by repeating the above step.
2How to Partition a Flash Drive on Mac?
If you want to partition your flash drive on your Mac, then you will be glad to know that it is possible. On Mac, you can do this via Disk Utility.
Steps to Partition Flash Drive on Mac
Follow these instructions to partition flash drive on Mac:
Step 1. On your Mac, open Disk Utility. And connect your flash drive to your Mac.
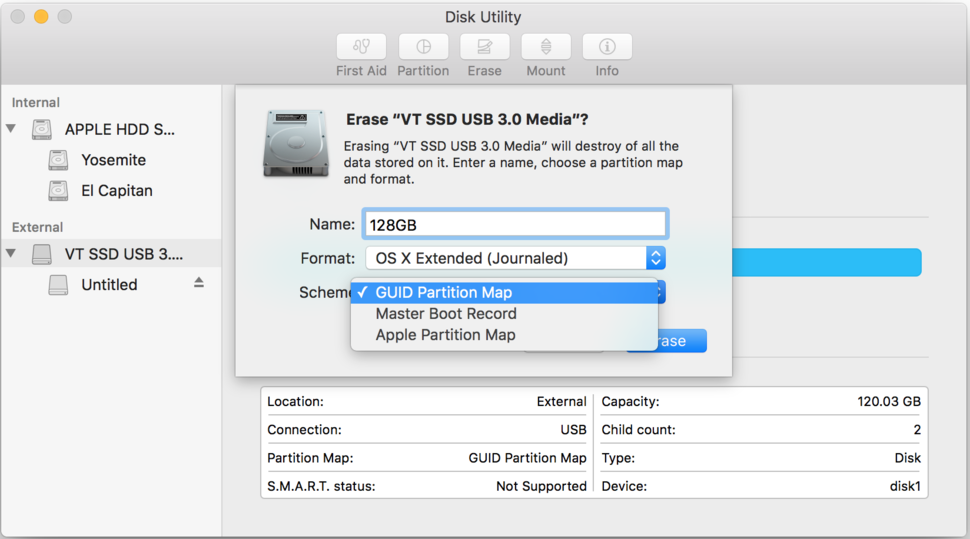
Step 2. Once the Disk Utility is opened, select your flash drive from the sidebar and click the Erase button.
Step 3. On the newly opened window, select OS X Extended (Journaled) from the Format menu.
Step 4. Make sure to click on Scheme > GUID Partition Map. Next, format the drive via the Erase option.
Step 5. After formatting, click the Partition button and then use the '+' button to create and add additional partitions. Add as many partitions as you like.
Step 6. After setting the sizes, labels, etc. to partitions, click Apply to confirm your action. Partitions will be created.
Bonus Tip 1. Best Way to Recover Files from Flash Drive after Partition or Format
It's wise to backup the data on your flash drive before partitioning or formatting it. So, what to do if you forgot this or some important files were left when made a backup? Don't worry, a powerful data recovery tool can help you find them back!
iMyFone AnyRecover is one of such popular data recovery tools. It can help you find all your lost files no matter how you lost them. Files recovery at a formatted or partitioned USB flash drive is easy as 1-2-3 with AnyRecover.
Key FeaturesRecover lost files from different data loss scenarios, including formatted data recovery, deleted files recovery, formatted device recovery, etc.
Recover over 1000 type of files, including photos, videos, audios, emails, documents, archives and more.
Recover files from various storage mediums, such as USB flash drive, hard drive, SD card, digital camera, computer, etc.
Differing from other recovery tools, AnyRecover is 100% safe to use, it won't do any damage to your existing data.
One of the most reliable data recovery software with high data recovery rate - Up to 98%.
Steps to Recover Files from Flash Drive after Partition or Format
Step 1. Open AnyRecover on your computer, then connect your Flash Drive to your computer, select it.
Step 2. After selecting the location, hit “Start” button to start the process.
Best Partition Scheme Mac

Step 3. After scanning, preview and select the files, then click on Recover button to get the lost files back.
Bonus Tip 2. Best USB Flash Drive for Windows & Mac
Among many quality flash drives, SanDisk Extreme PRO 128 GB Drive is considered the most popular USB flash drive for Windows and Mac. Following are the top features of this USB flash drive:
Blistering speeds: 380 MB/s write, 420 MB/s read.
Durable, sleek, and eye-catching aluminum casing design.
AES, 128-bit file encryption for excellent security for sensitive files.
USB 3.0 as well as backward compatibility with USB 2.0.
Lifetime warranty.
Best Mac Scheme Partition List
For new users, personal Debian boxes, home systems, and othersingle-user setups, a single / partition (plusswap) is probably the easiest, simplest way to go. However, if yourpartition is larger than around 6GB, choose ext3 as your partitiontype. Ext2 partitions need periodic file system integrity checking,and this can cause delays during booting when the partition is large.
For multi-user systems or systems with lots of disk space, it's bestto put /var,/tmp, and /home each ontheir own partitions separate from the /partition.
You might need a separate /usr/local partition ifyou plan to install many programs that are not part of the Debiandistribution. If your machine will be a mail server, you might needto make /var/mail a separate partition. Often,putting /tmp on its own partition, for instance20–50MB, is a good idea. If you are setting up a server with lotsof user accounts, it's generally good to have a separate, large/home partition. In general, the partitioningsituation varies from computer to computer depending on its uses.
For very complex systems, you should see theMulti Disk HOWTO. This contains in-depth information, mostlyof interest to ISPs and people setting up servers.
With respect to the issue of swap partition size, there are manyviews. One rule of thumb which works well is to use as much swap asyou have system memory. It also shouldn't be smaller than 16MB, inmost cases. Of course, there are exceptions to these rules. If youare trying to solve 10000 simultaneous equations on a machine with256MB of memory, you may need a gigabyte (or more) of swap.
On some 32-bit architectures (m68k and PowerPC), themaximum size of a swap partition is 2GB. That should be enough fornearly any installation. However, if your swap requirements are thishigh, you should probably try to spread the swap across differentdisks (also called “spindles”) and, if possible, different SCSI orIDE channels. The kernel will balance swap usage between multipleswap partitions, giving better performance.
As an example, an older home machine might have 32MB of RAM and a1.7GB IDE drive on /dev/sda. There might be a500MB partition for another operating system on/dev/sda1, a 32MB swap partition on/dev/sda3 and about 1.2GB on/dev/sda2 as the Linux partition.
For an idea of the space taken by tasksyou might be interested in adding after your system installation iscomplete, check Section D.2, “Disk Space Needed for Tasks”.
